Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculation
VMware vSphere 4.1 - HA Admission Control Slot Calculation. Posted on 07 Feb 2011 by Ray Heffer. VMware HA (High Availability) admission control is something I wanted to understand better so I started making notes gathered from various sources on the subject, and in particular the way slot sizes are calculated. In vSphere 5.1, you can set these values in the cluster settings in the vSphere Web Client, under Slot Size policy and Fixed slot size. Note: Configuration this way sets the exact value. To set the slot size: In the vSphere Web Client, browse to the vSphere HA cluster. Click the Manage tab and click Settings. Under Settings, select HA and click.
- Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculation Chart
- Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculation Formula
- Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculation Calculator
- Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculations
- Vmware Ha Slot Size Calculation
VMWare vShpere Slot Calculation
As per VMWare's Definition,
'A slot is a logical representation of the memory and CPU resources that satisfy the requirements for any powered-on virtual machine in the cluster.'
If you have configured reservations at VM level, It influence the HA slot calculation. Highest memory reservation and highest CPU reservation of the VM in your cluster determines the slot size for the cluster.
Here is the Example,
If you have the VM configured with the highest memory reservation of 8192 MB (8 GB) and highest CPU reservation of 4096 MHZ. among the other VM's in the cluster, then the slot size for memory is 8192 MB and slot size for CPU is 4096 MHZ. in the cluster.
If no VM level reservation is configured , Minimum CPU size of 256 MHZ and memory size of 0 MB + VM memory overhead will be considered as CPU and Memory slot size.
Calculation for Number of Slots in cluster :-
Once we got the Slot size for memory and CPU by the above method , Use the below calculation
Num of CPU Slots = Total available CPU resource of ESX or cluster / CPU Slot Size
Num of memory slots = Total available memory resource of ESX or cluster minus memory used for service console & ESX system / Memory Slot size
Let's take a Example,
I have 3 host on the cluster and 6 Virtual machine is running on the cluster and Each host capacity as follows
RAM = 50 GB per Host
CPU = 8 X 2.666 GHZ per host
Cluster RAM Resources = 50 X 3 = 150 GB - Memory for service console and system = 143 GB
Cluster CPU resources = 8 X 2.6 X 3 = 63 GHZ (63000 MHZ) of total CPU capacity in the cluster - CPU Capacity used by the ESX System = 60384 MHZ
I don't have any memory or CPU reservation in my cluster, So, the default CPU slot size 256 MHZ and one of my Virtual machine is assigned with 8 vcpu and its memory overhead is 344.98 MB (which is the highest overhead among my 6 virtual machines in the cluster)
Let's calculate the num of CPU & Memory slots
Num of CPU Slots = Total available CPU resource of cluster / CPUSlot size in MHZ
No of CPU Slots = 60384 MHZ / 256 MHZ = 235.875 Approx
Num of Memory Slots = Total available Memory resource of cluster / memory Slot Size in MB
Num of Memory Slots = 146432 / 345 = 424 Approx
The most restrictive number among CPU and Memory slots determines the amount of slots for this cluster. We have 235 slots available for CPU and 424 Slots available for Memory. So the most restrictive number is 235.
So, Total number of slots for my cluster is 235 Approx. Please find the below snapshot
Please refer my blog post on Understanding Total Slots, Used Slots & Available slots in VMware HA Slot to understand Total Slots, Used Slots & Available slots
I hope you understand the post..Thanks For Reading !!!!!
Recently I have been asked by my customers and also blog readers 🙂 about VMware HA Admission Control. As this topic is often misunderstood, this post covers some information about this important feature of VMware vSphere HA.
In this post you will find answers for the following questions:
- What is Admission Control?
- What is and how to check slote size?
- When and which Admission Control Policy should I use? How to solve Insufficient Resources for HA failover?
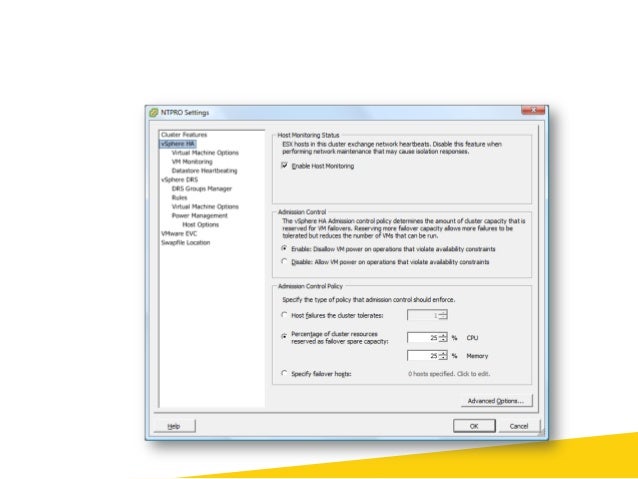
Admission control is used to ensure that sufficient resources are available in a cluster to provide failover protection and to ensure that virtual machine resource reservations are respected. There are three Admission control policies:
- Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved Admission Control Policy
- Host Failures Cluster Tolerates Admission Control Policy
Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculation Chart
It's very important to mention that Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved and Host Failures Cluster Tolerates are based on CPU and memory reservations at Virtual Machine (VM) level (it ignores resource pools reservation settings). But only? Nope, also overhead reservation is taken into considerations. So the formula is:
Configured Reservation for VM + Overhead Reservation
Overhead Reservation depends on VM configuration and usage (for example: RAM, devices etc). It means that for a large VMs with not configured reservation (equals 0), there is a noticeable Overhead Reservation!
Specify Failover Hosts
The easiest option (it does not mean the best 🙂 ) of Admission Control. vSphere HA attempts to restart its virtual machines on one of the specified failover hosts.
Host Failures Cluster Tolerates
With the Host Failures Cluster Tolerates admission control policy, vSphere HA uses slot to ensure that a specified number of hosts can fail and sufficient resources remain in the cluster to fail over all the virtual machines from those hosts.
Slot is a logical representation of CPU and memory. Depending on vSphere version, the default slot size is 0 MB of RAM and 256 MHz CPU (4.1 and earlier) or 0 MB of RAM and 32Mhz (5.0 and later).
The admission control is performed by VMware HA with the following steps:
- Calculates the slot size (based on powered-on VMs and selections the largest value).
- Determines how many slots each host in the cluster can hold.
- Determines the Current Failover Capacity of the cluster.
- Determines whether the Current Failover Capacity is less than the Configured Failover Capacity.
So let's make an example. As shown on the above figure, we have three ESXi hosts each with a different amount of available CPU and memory resources:


- ESXi1 - 9GB of RAM and 9Ghz of CPU
- ESXi2 - 6GB of RAM and 9Ghz of CPU
- ESXi3 - 6GB of RAM and 6Ghz of CPU
There are five powered-on VMs:
- VM1 and VM2 - 1GB of RAM and 2GHz of CPU
- VM3 - 2GB of RAM and 1GHz of CPU
- VM4 and VM5 - 1GB of RAM and 1GHz of CPU
As mentioned earlier, the slot size is the largest value so in this example: the slot size is 2GHz of CPU and 2GB of memory.
So how many slots are available per hosts?
- ESXi1 - 3 slots
- ESXi2 - 3 slots
- ESXi3 - 4 slots
If ESXi3 host fails, we have available 6 slots (3+3) so sufficient resources are available in a cluster to provide failover protection (one slot available yet to create).
Since vSphere 5.x, it is possible to configure the default slot size via Web Client:
If you use Standard Client or vSphere 4.x, you need to change some advanced parameters such as das.slotmeminmb and das.slotcpuinmhz. For more information please follow VMware KB here.
Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved
The Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved works different - vSphere HA ensures that a specified percentage of aggregate CPU and memory is reserved for failover.
The admission control is performed by VMware HA with the following steps:
- Calculates the total resource requirement for all powered on machines in the cluster.
- Calculates the total host resources available for the virtual machines.
- Calculates the current CPU and Memory failover capacity for the cluster (specified by administrator).
- Determines if either the current CPU failover or current memory failover is less than the corresponding failover capacity.
Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculation Formula
As shown on the above figure, there are five VMs and three ESXi hosts and the total VMs requirements for the powered-on VMs is 6GB of RAM and 7GHz of CPU. To calculate the Current CPU Failover Capacity we use the following formula:
Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculation Calculator
(Total host resources - Total VMs requirements) / Total host resources
so CPU: (24-7) / 24 = 70% and Memory: (21-6) / 21 = 71%
Vsphere Ha Slot Size Calculations
If you specify 33% CPU and Memory Failover Capacity, you have around 35% of resource available for new VMs yet 🙂

Insufficient Resources for HA failover
Sometimes you can get the following error during configuring vSphere HA with Admission Control enabled:
Insufficient Resources for HA failover
In most of all cases, the above error can happen when you configure Host Failures Cluster Tolerates Admission Control policy. Why? For example you have a large VM (with large reservation so slot size is also large) and when vSphere HA calculates powered on VMs and available slots on all ESXi hosts, it can be a situation when sufficient resources are not available in a cluster to provide failover protection. To solve this problem you should revise the VMs reservations or reconfigure Admission Control to use the Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved policy.
When and which Admission Control Policy should I use?
Vmware Ha Slot Size Calculation
Generally I use the Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved policy because it's much simpler and more flexible than Host Failures Cluster Tolerates Admission Control policy. Of course, you have to remember that when you add or remove ESXi hosts from your cluster, you need to reconfigure percentages. Also if you have an unbalanced vSphere Cluster you should use the Percentage of Cluster Resources Reserved policy.
Conclusion
I hope that Admission Control is understandable for you now 🙂 For more information (much deeper) please follow a fantastic book written by Duncan Epping: VMware vSphere 5.1 Clustering Deepdive 🙂